Position sizing is one of the most crucial aspects of successful forex trading, yet it’s often misunderstood or overlooked by both new and experienced traders. While a solid trading strategy, disciplined mindset, and a good grasp of market analysis are essential, how much you risk on each trade can ultimately determine your long-term profitability—or lead to ruin.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the principles of professional position sizing in forex trading, explain why it matters, and provide a step-by-step guide to calculating optimal trade sizes based on risk tolerance, account size, and market conditions.
What Is Position Sizing in Forex?
Position sizing refers to determining the number of lots or units you trade on a position, based on the amount of capital you’re willing to risk and the size of your stop loss. In simple terms, it answers the question: “How big should my trade be?”
Correct position sizing ensures that you don’t risk too much of your capital on a single trade, which helps preserve your account during drawdowns. It also allows consistent risk exposure across different trades, promoting better risk-adjusted performance over time.
Why Position Sizing Matters
Many traders focus heavily on trade entries and technical indicators but ignore position sizing, treating it as an afterthought. This is a critical mistake. Here’s why:
- Capital Preservation: Even the best strategies have losing streaks. Proper position sizing keeps you from blowing your account during those periods.
- Risk Consistency: With consistent position sizing, you’re able to apply a systematic and repeatable approach to risk, which is key to evaluating your strategy’s effectiveness.
- Emotional Stability: Knowing your risk is controlled reduces emotional interference. You’re less likely to panic, revenge trade, or abandon your system after losses.
- Scalability: Good position sizing techniques make it easier to grow and scale your account while maintaining the same level of risk.
Key Concepts for Position Sizing
Before we dive into the calculation process, let’s define a few important terms that underpin position sizing in forex:
1. Account Balance
The total amount of capital in your trading account. It’s typically used as the base for calculating your maximum allowable risk per trade.
2. Risk Per Trade
The percentage of your account balance you are willing to lose on a single trade. Most professional traders risk 1% or less per trade, with a common rule of thumb being 0.5%–2%.
3. Stop Loss Size
The number of pips between your entry and your stop-loss level. The wider your stop, the smaller your position should be to keep your dollar risk constant.
4. Pip Value
The monetary value of a single pip movement in your position. Pip value depends on the currency pair being traded, the size of your position (lot size), and the base currency of your account.
Step-by-Step Guide to Proper Position Sizing
Let’s walk through the process of determining the correct position size using a real-world example.
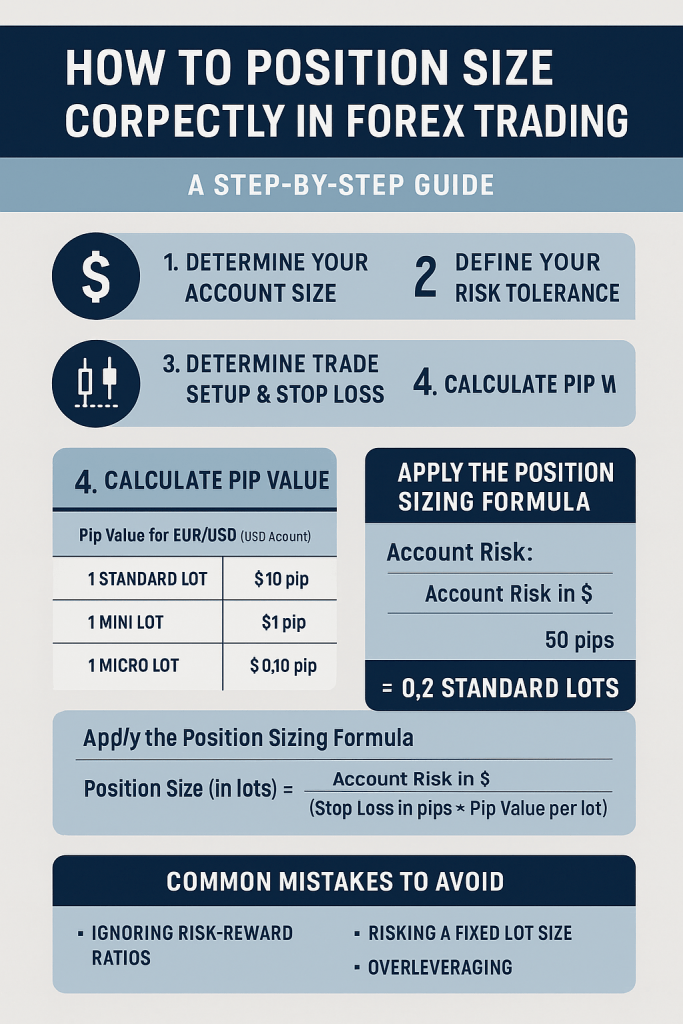
Step 1: Determine Your Account Size
Assume your trading account balance is $10,000.
Step 2: Define Your Risk Tolerance
Let’s say you’re willing to risk 1% per trade, or $100 on this trade.
Step 3: Determine the Trade Setup and Stop Loss
You identify a trade setup on EUR/USD and decide to place a 50-pip stop loss based on recent price action.
Step 4: Calculate Pip Value for the Trade
If you’re trading EUR/USD with a USD-denominated account:
- 1 standard lot (100,000 units) = $10 per pip
- 1 mini lot (10,000 units) = $1 per pip
- 1 micro lot (1,000 units) = $0.10 per pip
We need to figure out how many lots result in $100 of risk when the stop loss is 50 pips.
Step 5: Apply the Position Sizing Formula
Use this formula:Position Size (in lots) = (Account Risk in $) / (Stop Loss in pips × Pip Value per lot)
Plug in the values:= $100 / (50 pips × $10 per pip for standard lot) = $100 / $500 = 0.2 standard lots
So, the correct position size is 0.2 standard lots, or 2 mini lots.
This means if the trade hits your stop loss, you lose $100, or 1% of your account—exactly what you intended.
How Currency Pair Affects Pip Value
For some pairs, especially cross currencies (like GBP/JPY or EUR/GBP), pip value calculation differs due to the quote currency not matching your account base currency. Use pip value calculators or formulas to get accurate results.
For example, for GBP/JPY:
- 1 pip = 0.01 movement
- If the current price is 160.00 and you’re trading 1 standard lot, pip value = roughly £10, which must be converted to USD if your account is in USD.
Always verify pip value before sizing trades in exotic or cross currency pairs.
Using a Position Size Calculator
Manual calculations are great for understanding the concept, but in practice, most traders use a position size calculator. These are widely available for free online and can calculate position size in seconds based on your:
- Account currency
- Risk percentage
- Stop loss in pips
- Currency pair
Reliable tools include:
- Myfxbook Position Size Calculator
- Babypips Position Size Calculator
- MetaTrader add-ons and trading journal software
Advanced Position Sizing Techniques
1. Fixed Fractional Position Sizing
This is the standard method discussed above—risking a fixed percentage of your capital per trade.
2. Fixed Dollar Position Sizing
Here you risk a fixed dollar amount regardless of account size. It’s simple but doesn’t scale well as your account grows or shrinks.
3. Volatility-Based Sizing
This method adjusts position size based on market volatility (e.g., using the ATR indicator). Higher volatility means smaller positions to keep dollar risk in check.
4. Kelly Criterion
A mathematical formula for optimal bet sizing based on historical win rate and risk-reward ratio. While theoretically sound, it can result in overly aggressive sizing and is best used with caution or modified versions.
5. Scaling In/Out
This involves entering a position in parts (scaling in) or taking profit in stages (scaling out). It adds flexibility but requires experience and strict rules.
Common Position Sizing Mistakes to Avoid
1. Ignoring Risk-Reward Ratios
Position sizing works best when combined with good risk-reward setups. Avoid trades where the potential reward is smaller than your risk.
2. Trading Without a Stop Loss
Without a stop, position sizing becomes meaningless—you have no defined risk.
3. Risking a Fixed Lot Size
Many traders always trade 1 lot or 0.1 lots regardless of stop loss size. This results in inconsistent and often excessive risk.
4. Overleveraging
Forex brokers offer high leverage (up to 500:1), tempting traders to go big. But overleveraging can blow your account even with a small adverse move.
Conclusion
Position sizing is not just a technical detail—it’s the foundation of sound risk management in forex trading. No matter how accurate your analysis or how strong your strategy, incorrect position sizing can sabotage your trading performance.
By sizing your trades correctly using your account balance, risk tolerance, and stop loss size, you take control of your risk and give your trading strategy the room it needs to succeed.
Here’s a quick checklist for professional position sizing:
- Always define your risk per trade before entering.
- Adjust your position size based on stop loss and pip value.
- Use a position size calculator for accuracy and speed.
- Incorporate volatility-based or advanced techniques as your experience grows.
- Stay consistent—discipline beats excitement in trading every time.
Remember: In trading, it’s not about how often you’re right, but how well you manage risk when you’re wrong. Master position sizing, and you’ll already be ahead of most retail traders.
